Selection of an antidepressant treatment should consider both efficacy and tolerability[1]
Explore the comparative efficacy and tolerability of 18 antidepressants, including Brintellix® (vortioxetine)1
Grouped into various classes of drugs with varying mechanisms of action, antidepressants are widely used treatments for major depressive disorder (MDD).1 Prescription of antidepressants should be informed by the best available evidence to make the best choice for each individual patient.1 Network meta-analyses of existing datasets make it possible to estimate comparative efficacy, summarise and interpret the wider picture of the evidence base, and to understand the relative merits of the multiple interventions.1
A large network meta-analysis including 522 placebo-controlled and head-to-head trials and 116,477 patients compared 21 antidepressants in the acute treatment of MDD in adults, providing perspectives on the comparative efficacy† and acceptability‡ of 21 commonly prescribed antidepressants used for the acute treatment of adults with MDD.1
Explore the analysis of the head-to-head studies comparing 18 antidepressants§ in more detail below.
Meta-analysis of head-to-head studies comparing the efficacy† and acceptability‡ of 18 antidepressants§1
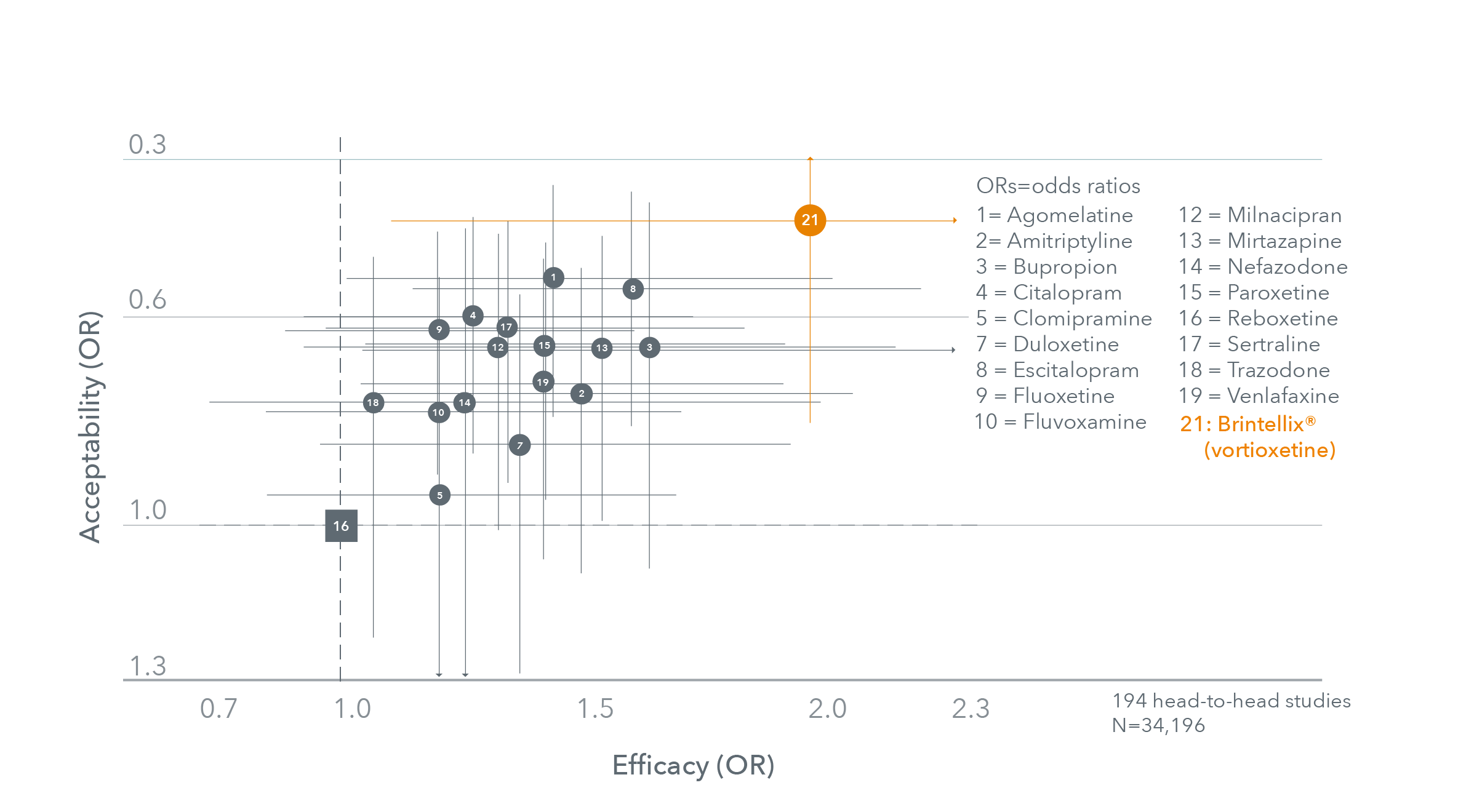
Adapted from: Cipriani A et al. 20181
Data are reported as ORs in comparison with reboxetine, which is the reference drug.
Error bars are 95% credible intervals.
Considering all placebo-controlled and head-to-head studies. Brintellix® showed similar efficacy† and acceptability‡ vs. other antidepressants.1 All antidepressants were shown to be more effective than placebo.1
Adapted from: Cipriani A et al. 20181
Data are reported as ORs in comparison with reboxetine, which is the reference drug.
Error bars are 95% credible intervals.
Considering all placebo-controlled and head-to-head studies. Brintellix® showed similar efficacy† and acceptability‡ vs. other antidepressants.1 All antidepressants were shown to be more effective than placebo.1


* Fictitious patient quote.
† Antidepressive response was defined by a reduction of >50% of the total score on a standardised observer scale for depression (HAM-D or MADRS).
‡ Acceptability was defined based on all-cause discontinuation of the treatments.
§ A network meta-analysis of only head-to-head studies included a single direct study comparison of Brintellix® at a dose of 10 mg/day and venlafaxine at a dose of 150 mg/day. The error bars, indicating 95% credibility intervals, reflect limited data for Brintellix® in this network meta-analysis.1
Abbreviations:
HAM-D, Hamilton depression rating scale; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; OR, odds ratio.
* Fictitious patient quote.
† Antidepressive response was defined by a reduction of >50% of the total score on a standardised observer scale for depression (HAM-D or MADRS).
‡ Acceptability was defined based on all-cause discontinuation of the treatments.
§ A network meta-analysis of only head-to-head studies included a single direct study comparison of Brintellix® at a dose of 10 mg/day and venlafaxine at a dose of 150 mg/day. The error bars, indicating 95% credibility intervals, reflect limited data for Brintellix® in this network meta-analysis.1
Abbreviations:
HAM-D, Hamilton depression rating scale; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg depression rating scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; OR, odds ratio.

