Real-World Evidence: MDD Patients on Brintellix®(vortioxetine) showed significant remission rate with reduction of concomitant medication
The REVIDA study aimed to assess the evolution of symptoms of MDD in South-East Asian (SEA) patients treated with Brintellix® in real-world clinical practice. Patients (N=138) with an active episode of MDD were recruited across 4 countries (Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand) and initiated with Brintellix® treatment (flexibly dosed up to 20mg/day) for a period of 3 months.1
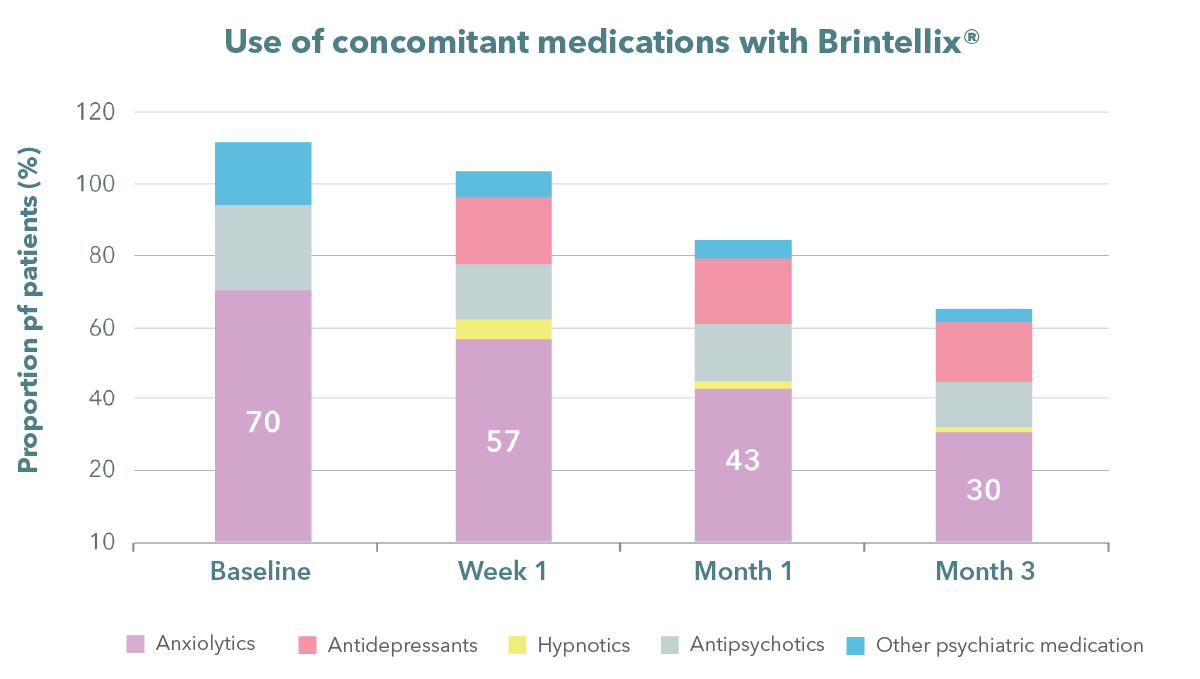
Note: Patients may have one or more concomitant psychiatric medications under specific visit; Percentages were
based on the number of patients in the safety population and may not add up to 100%
Chin CN et al. Curr Med Res Opin 2018;34:1975-1984
Anxiolytics are commonly used with antidepressants when managing MDD patients. In the REVIDA study, patients with MDD who were using high levels of anxiolytics (predominantly benzodiazepines) were able to taper off their use of benzodiazepines within 3 months of using Brintellix®.2 Additionally, treatment with Brintellix® resulted in greater than 50% remission rates†, coupled with improvements in work productivity‡ by Month 3.1
Note: Patients may have one or more concomitant psychiatric medications under specific visit; Percentages were
based on the number of patients in the safety population and may not add up to 100%
Chin CN et al. Curr Med Res Opin 2018;34:1975-1984
Anxiolytics are commonly used with antidepressants when managing MDD patients. In the REVIDA study, patients with MDD who were using high levels of anxiolytics (predominantly benzodiazepines) were able to taper off their use of benzodiazepines within 3 months of using Brintellix®.2 Additionally, treatment with Brintellix® resulted in greater than 50% remission rates†, coupled with improvements in work productivity‡ by Month 3.1
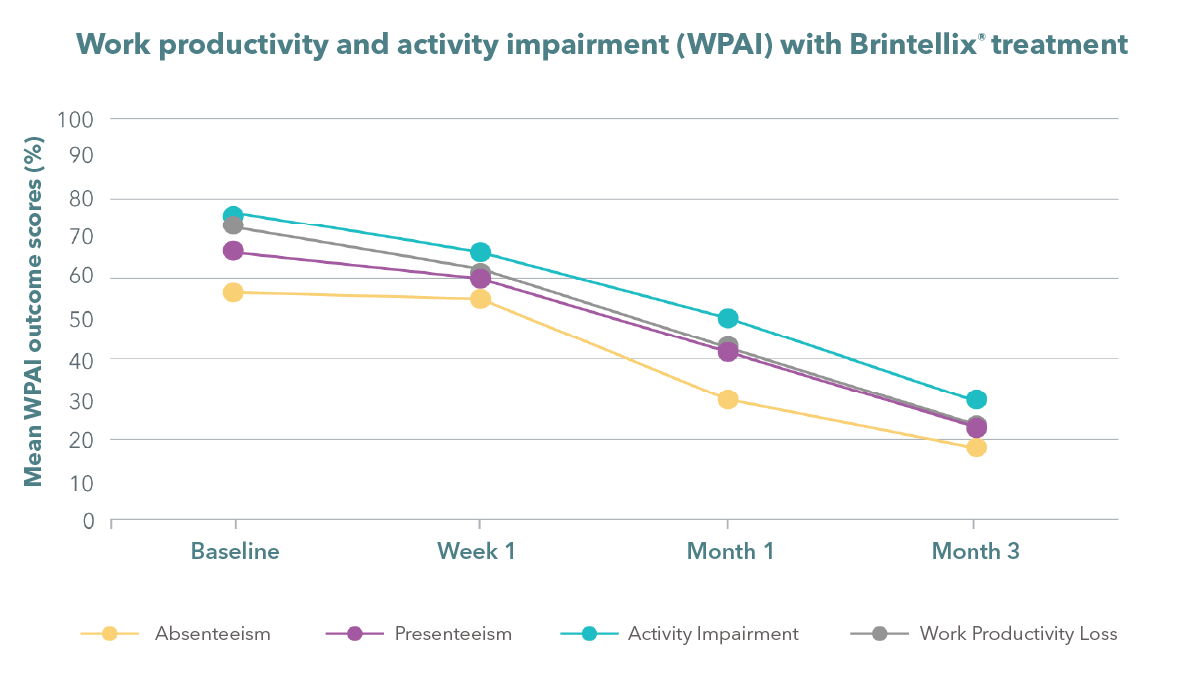
Absenteeism – percentage of work time missed. Presenteeism – percentage of work impairment when present.
Work productivity loss – percentage of overall work impairment.
Activity impairment – percentage of overall activity impairment
Chin CN et al. Curr Med Res Opin 2018;34:1975-1984.
Overall, Brintellix® was reported to be generally well-tolerated with low discontinuation rates in this real-world study.1 There were no unexpected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) reported, with the most common ADRs being abdominal discomfort (4 events) and nausea (3 events out of 138 patients).1 Notably, no adverse events of vomiting, sexual dysfunction or dry mouth were reported.1
Absenteeism – percentage of work time missed. Presenteeism – percentage of work impairment when present.
Work productivity loss – percentage of overall work impairment.
Activity impairment – percentage of overall activity impairment
Chin CN et al. Curr Med Res Opin 2018;34:1975-1984.
Overall, Brintellix® was reported to be generally well-tolerated with low discontinuation rates in this real-world study.1 There were no unexpected adverse drug reactions (ADRs) reported, with the most common ADRs being abdominal discomfort (4 events) and nausea (3 events out of 138 patients).1 Notably, no adverse events of vomiting, sexual dysfunction or dry mouth were reported.1

†Remission rate was defined as PHQ-9 score ≤4, CGI-S score ≤2
‡ work productivity was measured by the WPAI questionnaire
Abbreviations
REVIDA, REal-world study on Vortioxetine In patients with major Depression in South-East Asia; MDD, major depressive disorder; MDD, major depressive disorder; WPAI, work productivity and activity impairment; ADR, adverse drug reaction
†Remission rate was defined as PHQ-9 score ≤4, CGI-S score ≤2
‡ work productivity was measured by the WPAI questionnaire
Abbreviations
REVIDA, REal-world study on Vortioxetine In patients with major Depression in South-East Asia; MDD, major depressive disorder; MDD, major depressive disorder; WPAI, work productivity and activity impairment; ADR, adverse drug reaction

