The efficacy of Brintellix® increases with increasing dose response
With approximately 50% of patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) not responding adequately to initial antidepressant treatment‡2,3, guidelines recommend assessing treatment adherence or increasing to the maximum antidepressant dose that can be tolerated.4-7 The efficacy of Brintellix® (vortioxetine) increases with increasing dose, with 20 mg demonstrating greater improvements of depressive symptoms compared to 10 mg.†1,8
In a meta-analysis of six short-term, fixed dose, placebo-controlled studies, improvements across a broad range of depressive symptoms, as assessed with the MADRS single items, were seen for Brintellix® versus placebo across the dose range of 10 – 20 mg/day.1
The most pronounced therapeutic benefit across MDD symptoms is seen
with Brintellix® 20 mg, with statistically significant improvements vs placebo on all MADRS single items.1
Mean difference in change in MADRS single items at week 8 with Brintellix®§1
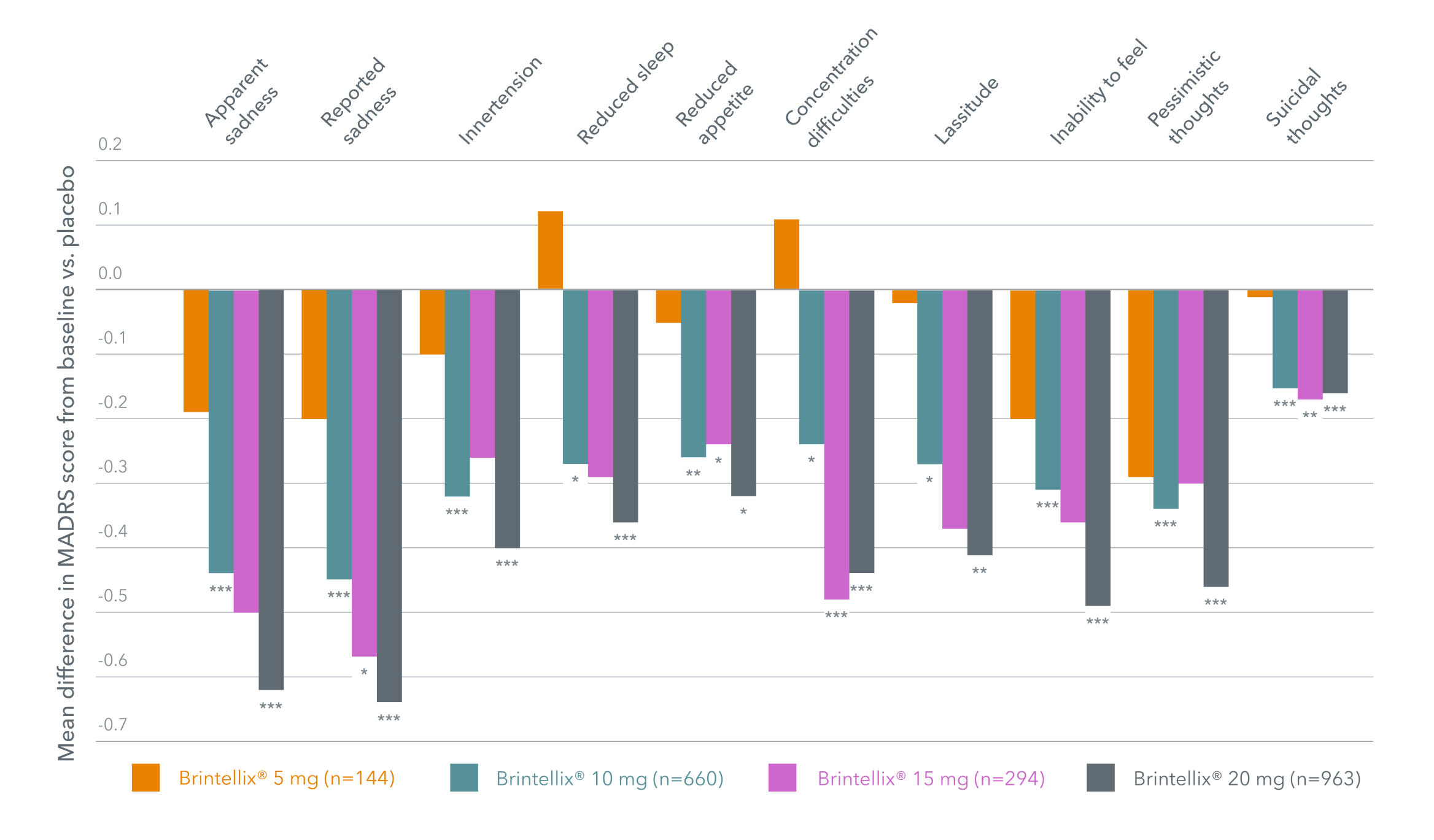
Adapted from Christensen MC et al. 2023.
§In these fixed-dose studies, patients who were assigned to receive Brintellix® 20 mg received a 10 mg dose for the first week of the 8-week study.1 *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
A clear dose response relationship for Brintellix® was confirmed in the meta-analysis in terms of improvement in MADRS total score at all timepoints, shown in the figure below.1 For Brintellix® 20 mg, significant differences in depressive symptoms¥ were observed vs placebo as early as 1 week after up-titration (i.e. Week 2 according to study design; p<0.05).1
Mean difference in change in MADRS total score from baseline in a meta-analysis§1
Adapted from Christensen MC et al. 2023.
§In these fixed-dose studies, patients who were assigned to receive Brintellix® 20 mg received a 10 mg dose for the first week of the 8-week study.1 *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
A clear dose response relationship for Brintellix® was confirmed in the meta-analysis in terms of improvement in MADRS total score at all timepoints, shown in the figure below.1 For Brintellix® 20 mg, significant differences in depressive symptoms¥ were observed vs placebo as early as 1 week after up-titration (i.e. Week 2 according to study design; p<0.05).1
Mean difference in change in MADRS total score from baseline in a meta-analysis§1
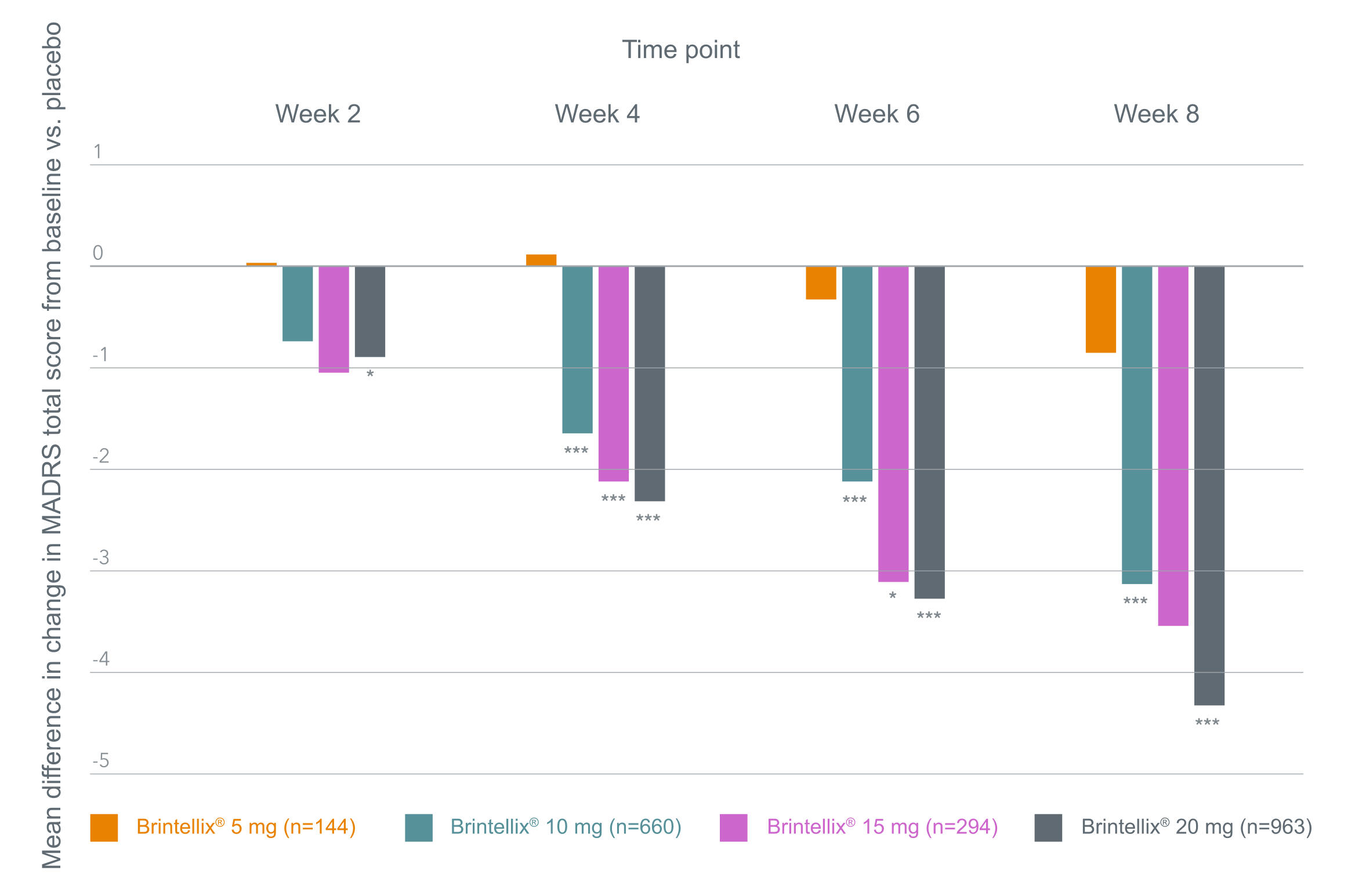
Adapted from: Christensen MC et al. 2023.
§In these fixed-dose studies, patients who were assigned to receive Brintellix® 20 mg received a 10 mg dose for the first week of the 8-week study.1 *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
Adapted from: Christensen MC et al. 2023.
§In these fixed-dose studies, patients who were assigned to receive Brintellix® 20 mg received a 10 mg dose for the first week of the 8-week study.1 *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.


† Depending on the individual patient response, the dose can be increased to a maximum of Brintellix® 20 mg or decreased to a minimum of 5 mg.8
‡ Response defined as ≥50% reduction in QIDS-SR16 score from baseline. Data taken from the STAR D study of 3671 patients treated at 41 different clinical sites.2,3
¥ As measured by the MADRS.1 When comparing two active treatments, a 1-point difference in MADRS total score is considered clinically relevant.9,10
Abbreviations: MADRS, Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; QIDS-SR, quick inventory of depressive symptomatology – self-report.
† Depending on the individual patient response, the dose can be increased to a maximum of Brintellix® 20 mg or decreased to a minimum of 5 mg.8
‡ Response defined as ≥50% reduction in QIDS-SR16 score from baseline. Data taken from the STAR D study of 3671 patients treated at 41 different clinical sites.2,3
¥ As measured by the MADRS.1 When comparing two active treatments, a 1-point difference in MADRS total score is considered clinically relevant.9,10
Abbreviations: MADRS, Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MDD, major depressive disorder; QIDS-SR, quick inventory of depressive symptomatology – self-report.

