Brintellix® is generally well tolerated †1
Brintellix® (vortioxetine) is generally well tolerated† in adult patients treated for major depressive disorder (MDD)1,2 and is less likely exhibiting many of the side effects typical of SSRIs and SNRIs.1
The table below is a comparison of prevalence rates of adverse events associated with commonly used antidepressants for treating MDD.1
Prevalence of adverse events among antidepressants1-5
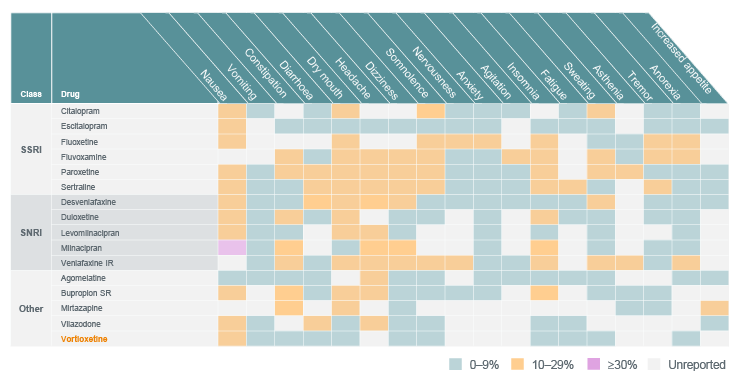
Adapted from: Lam RW. et al. 2024
SSRI = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, SNRI = serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
These guidelines recommend considering not only clinical factors when selecting an antidepressant, but also tolerability differences, including potential drug-drug interactions.1
Brintellix® has a low rate of adverse events6
Adapted from: Lam RW. et al. 2024
SSRI = selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, SNRI = serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
These guidelines recommend considering not only clinical factors when selecting an antidepressant, but also tolerability differences, including potential drug-drug interactions.1
Brintellix® has a low rate of adverse events6
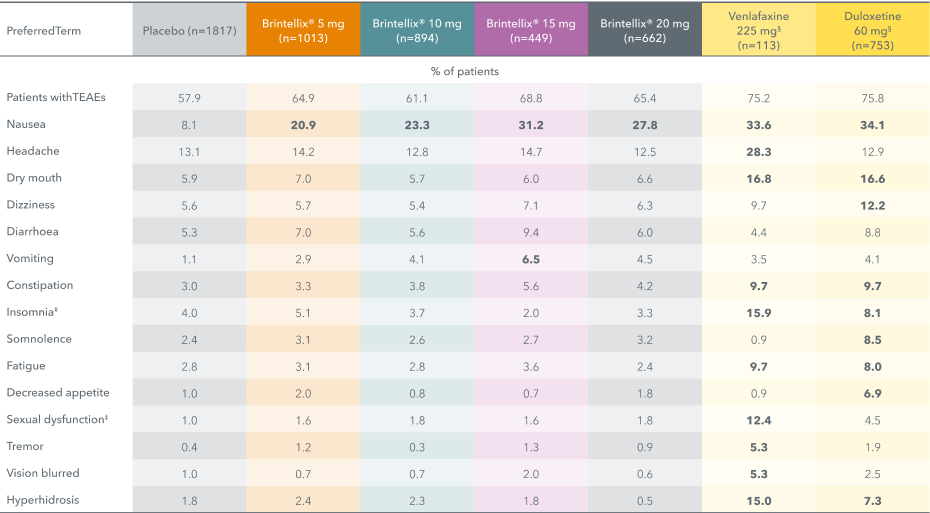
Adapted from: Baldwin DS et al. 2016a. % values in bold are ≥5% and >2 x placebo.
#Includes the preferred terms: insomnia, initial insomnia, middle insomnia, hyposomnia, sleep disorder, dyssomnia, poor quality sleep and terminal insomnia.
‡Includes the preferred terms: libido decreased, ejaculation delayed, ejaculation disorder, orgasm abnormal, anorgasmia, disturbance in sexual arousal, ejaculation failure, erectile dysfunction, loss of libido, orgasmic sensation decreased, sexual dysfunction, and vulvovaginal dryness.
§Duloxetine and venlafaxine were included as active references for study validation, not for comparison of effect size.
The most common adverse event reported with Brintellix® is nausea1,2,6, which is usually mild to moderate and does not generally lead to treatment discontinuation. It typically occurs within the first 2 weeks and is usually transient.2
Brintellix® has a low potential for drug-drug interactions and can be used with many common drugs including warfarin and aspirin, diazepam or combined oral contraceptives (ethinylestradiol 30 μg/levonorgestrel 150 μg).2
Adapted from: Baldwin DS et al. 2016a. % values in bold are ≥5% and >2 x placebo.
#Includes the preferred terms: insomnia, initial insomnia, middle insomnia, hyposomnia, sleep disorder, dyssomnia, poor quality sleep and terminal insomnia.
‡Includes the preferred terms: libido decreased, ejaculation delayed, ejaculation disorder, orgasm abnormal, anorgasmia, disturbance in sexual arousal, ejaculation failure, erectile dysfunction, loss of libido, orgasmic sensation decreased, sexual dysfunction, and vulvovaginal dryness.
§Duloxetine and venlafaxine were included as active references for study validation, not for comparison of effect size.
The most common adverse event reported with Brintellix® is nausea1,2,6, which is usually mild to moderate and does not generally lead to treatment discontinuation. It typically occurs within the first 2 weeks and is usually transient.2
Brintellix® has a low potential for drug-drug interactions and can be used with many common drugs including warfarin and aspirin, diazepam or combined oral contraceptives (ethinylestradiol 30 μg/levonorgestrel 150 μg).2

† Based on unadjusted rates from product monographs or summary of product characteristics of vortioxetine, citalopram, escitalopram and agomelatine.
Abbreviations:
CANMAT, Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments; MDD, major depressive disorder; SNRI, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.
† Based on unadjusted rates from product monographs or summary of product characteristics of vortioxetine, citalopram, escitalopram and agomelatine.
Abbreviations:
CANMAT, Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments; MDD, major depressive disorder; SNRI, serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor; SSRI, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor; TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event.

